The effects of alcohol are________. – The effects of alcohol are multifaceted, encompassing a wide range of physiological, cognitive, behavioral, social, and economic consequences. This comprehensive exploration delves into the profound impact of alcohol on individuals, communities, and society as a whole.
From impaired coordination and reduced heart rate to altered mood and impaired decision-making, alcohol’s physiological and cognitive effects are significant. Its role in social interactions, cultural practices, and economic burdens further highlights the complexity of alcohol’s influence.
Physiological Effects

Alcohol consumption can have significant physiological effects on the body, both in the short-term and long-term. These effects can range from impaired coordination and reduced heart rate to organ damage and other health issues.
Nervous System
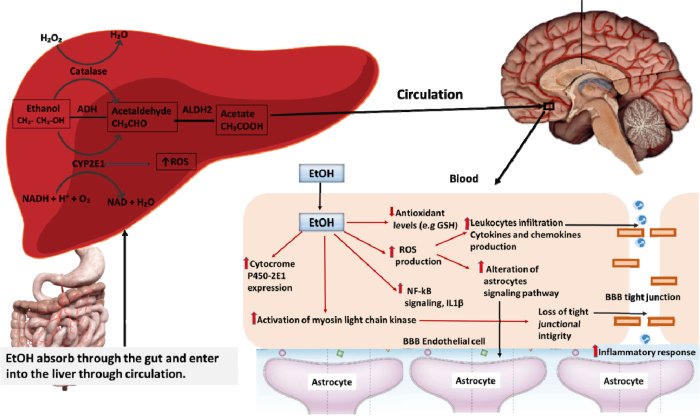
Alcohol is a depressant, which means it slows down the activity of the central nervous system. This can lead to a number of short-term effects, including impaired coordination, slurred speech, and slowed reaction times. In the long-term, heavy alcohol consumption can lead to damage to the brain and nervous system, including cognitive impairment and dementia.
Cardiovascular System
Alcohol can also affect the cardiovascular system. In the short-term, alcohol can cause blood pressure to increase and heart rate to decrease. In the long-term, heavy alcohol consumption can lead to heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular problems.
Digestive System
Alcohol can also affect the digestive system. In the short-term, alcohol can cause nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. In the long-term, heavy alcohol consumption can lead to liver damage, pancreatitis, and other digestive problems.
Cognitive and Behavioral Effects
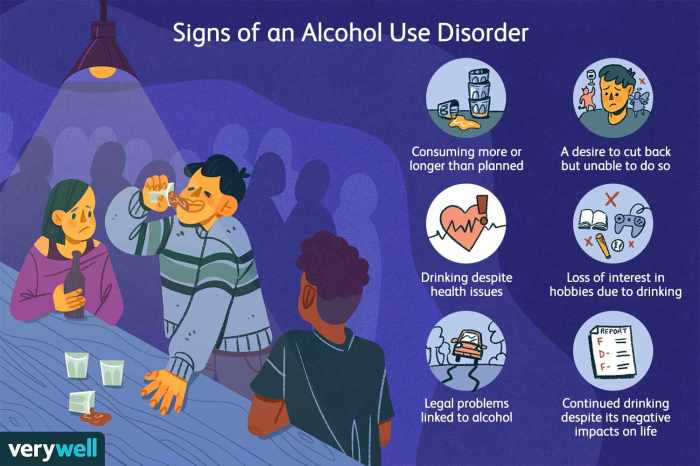
Alcohol has significant effects on cognitive functions, including memory, attention, and decision-making. It can impair these functions by interfering with the neurochemical processes in the brain responsible for these abilities. Alcohol can also alter mood, behavior, and social interactions, leading to disinhibition, reduced anxiety, and impaired judgment.
Mood and Behavior
Alcohol can have a variety of effects on mood and behavior, including:
- Euphoria and relaxation
- Reduced anxiety and inhibitions
- Increased talkativeness and sociability
- Impulsivity and aggression
- Mood swings and irritability
These effects are dose-dependent, meaning that they are more pronounced with higher levels of alcohol consumption. Alcohol can also interact with other drugs, such as stimulants and depressants, to produce unpredictable effects.
Alcohol Dependence
Alcohol dependence is a chronic condition that involves compulsive alcohol use despite negative consequences. It is characterized by:
- Tolerance, or the need for increasing amounts of alcohol to achieve the same effect
- Withdrawal symptoms, such as anxiety, tremors, and seizures, when alcohol use is stopped
- Cravings for alcohol
- Continued use of alcohol despite negative consequences, such as health problems, relationship problems, and job loss
Alcohol dependence can have a devastating impact on cognitive and behavioral functioning, leading to problems with memory, attention, decision-making, and social interactions. It can also increase the risk of accidents, injuries, and other health problems.
Social and Cultural Effects
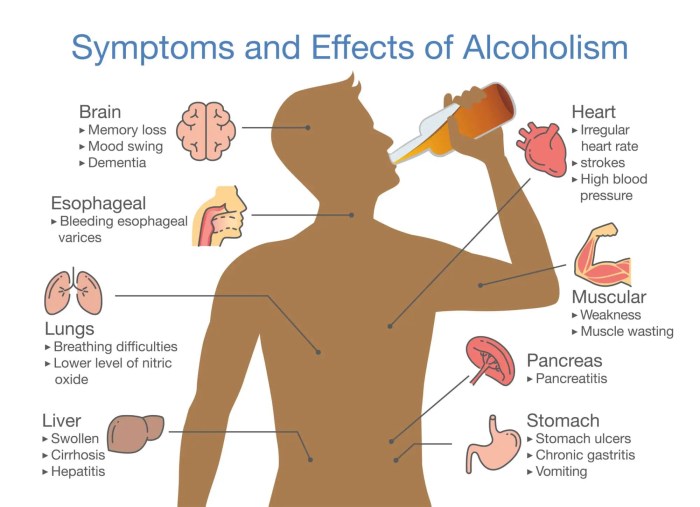
Alcohol has been deeply ingrained in human societies for centuries, playing a significant role in various social and cultural contexts. From celebratory gatherings to religious ceremonies, alcohol has been used to mark milestones, facilitate bonding, and enhance social interactions.However, the consumption of alcohol also carries potential risks and negative consequences.
Social stigma and discrimination associated with alcohol use and abuse can lead to marginalization and social isolation. Moreover, alcohol’s impact on family dynamics, relationships, and community well-being can be profound, contributing to domestic violence, financial instability, and increased healthcare costs.
Social Stigma and Discrimination
Alcohol use and abuse have long been associated with negative social perceptions and judgments. Individuals who engage in excessive drinking may face social isolation, discrimination, and even legal consequences. This stigma can prevent people from seeking help for alcohol-related problems, perpetuating a cycle of addiction and negative social outcomes.
Impact on Family Dynamics and Relationships, The effects of alcohol are________.
Alcohol use can significantly affect family dynamics and relationships. Excessive drinking can lead to conflicts, violence, and neglect within families. Children of alcoholic parents are more likely to experience emotional and behavioral problems, as well as an increased risk of developing alcohol use disorders themselves.
Impact on Community Well-being
Alcohol-related problems can have a detrimental impact on community well-being. Alcohol abuse is a major contributing factor to crime, violence, and accidents. It also places a significant burden on healthcare systems, law enforcement, and social services.
Economic and Public Health Effects
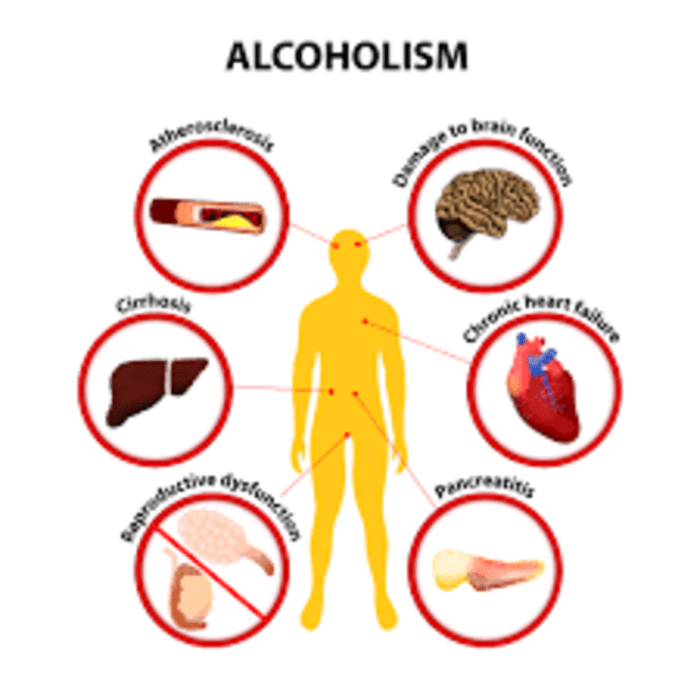
Alcohol consumption imposes significant economic and public health burdens on society. These effects range from healthcare expenses to lost productivity and crime, as well as contributions to accidents, injuries, and chronic diseases.
Healthcare Expenses
- Alcohol-related liver disease is a leading cause of hospitalization and liver transplantation.
- Alcohol abuse can lead to heart disease, stroke, and cancer.
- Alcohol-related mental health disorders, such as depression and anxiety, require significant treatment resources.
Lost Productivity
- Alcoholism can lead to absenteeism, presenteeism (reduced productivity while at work), and unemployment.
- Alcohol-related accidents and injuries can result in lost workdays and reduced earnings.
- Alcohol-related cognitive impairment can affect job performance and decision-making.
Crime
- Alcohol is a major contributing factor to violent crimes, including homicide, assault, and sexual assault.
- Alcohol-impaired driving is a leading cause of traffic accidents, injuries, and fatalities.
- Alcohol abuse can lead to property damage and theft.
Public Health
- Alcohol is a major risk factor for accidents, injuries, and falls.
- Alcohol consumption can contribute to chronic diseases, such as liver cirrhosis, heart disease, and cancer.
- Alcohol abuse can lead to mental health disorders, such as depression and anxiety.
FAQ: The Effects Of Alcohol Are________.
What are the short-term effects of alcohol consumption?
Short-term effects include impaired coordination, reduced reaction time, and impaired judgment.
How does alcohol affect cognitive function?
Alcohol can impair memory, attention, and decision-making abilities.
What is alcohol dependence?
Alcohol dependence is a condition in which an individual has a strong craving for alcohol and experiences withdrawal symptoms when they stop drinking.