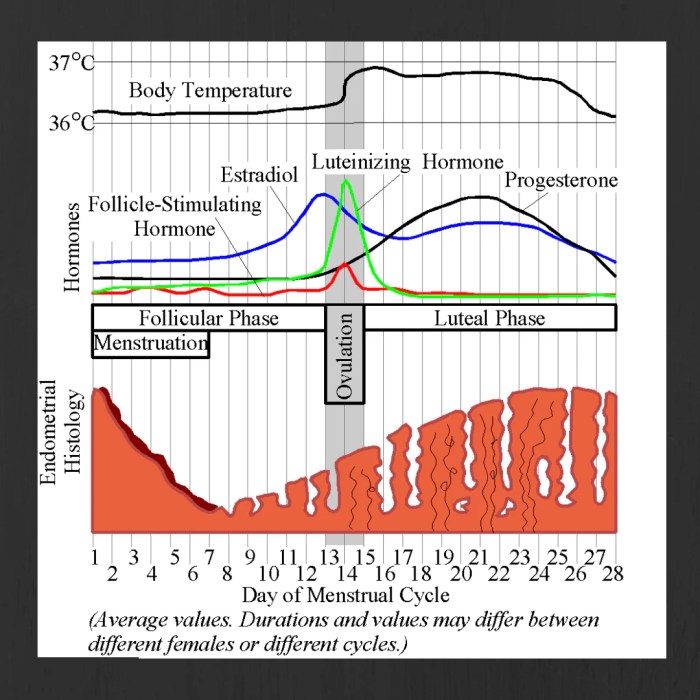
Embark on a scientific exploration with the menstrual cycle graphing lab #12 answer key, a comprehensive guide to understanding the intricacies of the menstrual cycle. This lab empowers individuals to monitor, analyze, and interpret their menstrual patterns, providing valuable insights into their reproductive health.
Through meticulously collected data and expert analysis, this lab unveils the hormonal fluctuations that orchestrate the menstrual cycle, empowering individuals to make informed decisions about their health and well-being.
Menstrual Cycle Graphing Lab #12
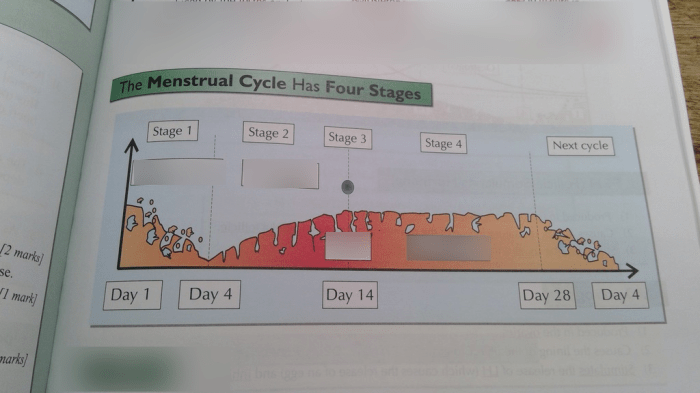
The Menstrual Cycle Graphing Lab #12 aims to provide students with a hands-on understanding of the menstrual cycle. By collecting and analyzing data on their own menstrual cycles, students can gain valuable insights into their reproductive health and identify potential patterns or irregularities.
Materials Required
- Menstrual cycle tracking chart or app
- Pencil or pen
- Graph paper or a spreadsheet program
Data Collection and Analysis
To collect data, students should begin tracking their menstrual cycles for at least three consecutive months. They should record the following information:
- First day of menstruation (day 1)
- Last day of menstruation
- Any spotting or discharge
- Physical symptoms (e.g., cramps, bloating, headaches)
- Emotional symptoms (e.g., mood swings, irritability, fatigue)
Once data has been collected, students can plot it on a graph. The x-axis of the graph should represent the days of the menstrual cycle, while the y-axis can be used to track different variables, such as cervical mucus, basal body temperature, or symptoms.
By identifying patterns and trends in the graph, students can gain insights into the different phases of their menstrual cycle. For example, they may notice that cervical mucus becomes more fertile around ovulation or that their mood swings tend to occur during the premenstrual phase.
Interpretation of Results, Menstrual cycle graphing lab #12 answer key
The hormonal changes that occur during the menstrual cycle have a significant impact on the data collected. For example, estrogen levels rise during the follicular phase, causing an increase in cervical mucus production. Progesterone levels rise during the luteal phase, causing a decrease in cervical mucus production and an increase in basal body temperature.
By understanding these hormonal changes, students can better interpret the results of their menstrual cycle graphs. They can identify the different phases of their cycle and gain insights into their reproductive health.
Applications and Limitations
Understanding the menstrual cycle has practical applications for women’s health. By tracking their cycles, women can:
- Identify their fertile window
- Plan for pregnancy or avoid conception
- Detect potential irregularities or health issues
However, it is important to note the limitations of menstrual cycle graphing. It is not a foolproof method for predicting ovulation or pregnancy. Additionally, some women may experience irregular cycles, which can make it difficult to track and interpret data.
Despite these limitations, menstrual cycle graphing can be a valuable tool for women to gain insights into their reproductive health. By understanding their own cycles, women can make informed decisions about their health and well-being.
Common Queries: Menstrual Cycle Graphing Lab #12 Answer Key
What is the purpose of the menstrual cycle graphing lab?
The menstrual cycle graphing lab aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the menstrual cycle by monitoring and analyzing hormonal changes and their impact on the body.
How does the lab help individuals understand their menstrual cycle?
The lab empowers individuals to track their menstrual patterns, identify trends, and correlate them with hormonal fluctuations, fostering a deeper understanding of their reproductive health.