Complete the Kw expression for the autoionization of water embarks on a captivating journey into the enigmatic realm of chemical reactions, where we unravel the intricacies of water’s remarkable ability to undergo self-ionization. This fundamental process holds profound implications for understanding the behavior of aqueous solutions and their significance in biological systems.
The equilibrium constant, Kw, emerges as a pivotal concept in this exploration, providing a quantitative measure of the extent to which water molecules undergo autoionization. By delving into the factors that influence Kw, such as temperature, ionic strength, and pH, we gain insights into the dynamic nature of water’s self-ionization.
Definition of Autoionization of Water
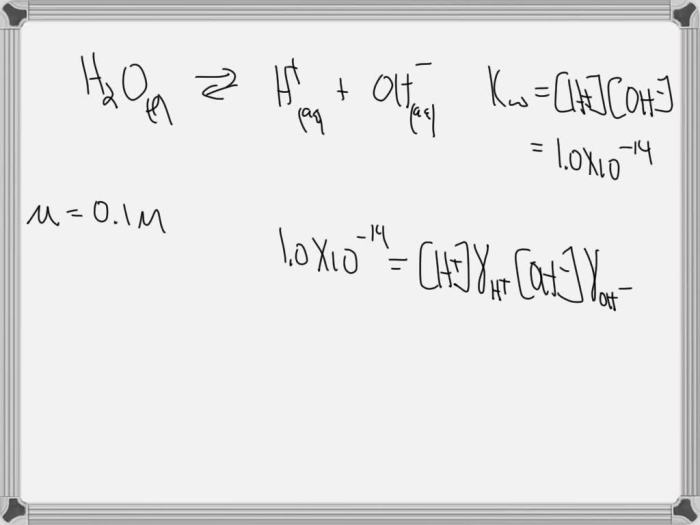
Autoionization of water is a chemical reaction in which water molecules spontaneously dissociate into hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH-).
The chemical equation for the autoionization of water is:
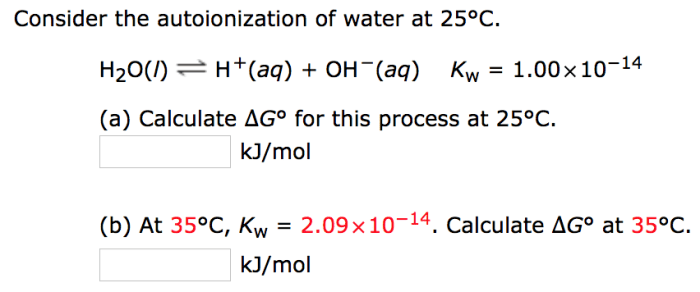
H2O (l) + H 2O (l) <=> H3O +(aq) + OH –(aq)
The equilibrium constant (Kw) for the autoionization of water is:
Kw = [H3O +][OH –]
Kw is a measure of the acidity or basicity of water. At 25 °C, Kw = 1.0 x 10 -14. This means that pure water is slightly acidic, with a pH of 7.0.
Factors Affecting Autoionization
Temperature
The equilibrium constant for the autoionization of water increases with increasing temperature. This means that water becomes more acidic as the temperature increases.
Ionic Strength
The ionic strength of a solution is a measure of the concentration of ions in the solution. The ionic strength of a solution affects the autoionization of water. High ionic strength decreases the autoionization of water, while low ionic strength increases the autoionization of water.
pH
The pH of a solution is a measure of the acidity or basicity of the solution. The pH of a solution affects the autoionization of water. Acidic solutions have a low pH and a high concentration of H 3O +ions.
Basic solutions have a high pH and a low concentration of H 3O +ions.
Applications of Autoionization
The autoionization of water is a fundamental chemical reaction that has many applications. Kw is used to calculate the pH and pOH of solutions. Kw is also used to determine the acidity or basicity of solutions.
- Calculating pH and pOH: The pH of a solution is a measure of the acidity or basicity of the solution. The pOH of a solution is a measure of the basicity of the solution. The pH and pOH of a solution can be calculated using the following equations:
- Determining the acidity or basicity of solutions: The acidity or basicity of a solution can be determined by comparing the pH of the solution to the pH of pure water. If the pH of a solution is less than 7, the solution is acidic. If the pH of a solution is greater than 7, the solution is basic.
pH =-log[H 3O +] pOH = -log[OH –]
Related Concepts
Dissociation Constants
The autoionization of water is related to the dissociation constants of acids and bases. The dissociation constant of an acid is a measure of the strength of the acid. The dissociation constant of a base is a measure of the strength of the base.
Self-Ionization
The autoionization of water is an example of self-ionization. Self-ionization is a chemical reaction in which a substance dissociates into ions in the absence of any other substance.
Importance in Biological Systems, Complete the kw expression for the autoionization of water
The autoionization of water is essential for life. The pH of biological fluids is tightly regulated by the autoionization of water. The autoionization of water also contributes to enzyme activity and cellular processes.
- pH balance: The pH of biological fluids is tightly regulated by the autoionization of water. The pH of blood is maintained at around 7.4. If the pH of blood changes too much, it can lead to serious health problems.
- Enzyme activity: The activity of many enzymes is dependent on the pH of the environment. The autoionization of water helps to maintain the pH of the environment within the optimal range for enzyme activity.
- Cellular processes: The autoionization of water contributes to many cellular processes, such as the transport of ions across cell membranes and the regulation of gene expression.
FAQ: Complete The Kw Expression For The Autoionization Of Water
What is the significance of the equilibrium constant, Kw, in the autoionization of water?
Kw quantifies the extent of water’s self-ionization, providing a measure of the concentration of hydronium and hydroxide ions in pure water.
How does temperature affect the autoionization of water?
As temperature increases, the autoionization of water increases, resulting in a higher concentration of hydronium and hydroxide ions.
What is the relationship between Kw and the pH of a solution?
Kw is inversely related to the pH of a solution. A higher Kw indicates a lower pH, signifying a more acidic solution.