As the topic of differences between christianity judaism and islam venn diagram takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers with gaya akademik dengan tone otoritatif into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
This comprehensive analysis will delve into the core beliefs, practices, and historical development of these three major world religions, illuminating their similarities and differences through the lens of a meticulously designed Venn diagram.
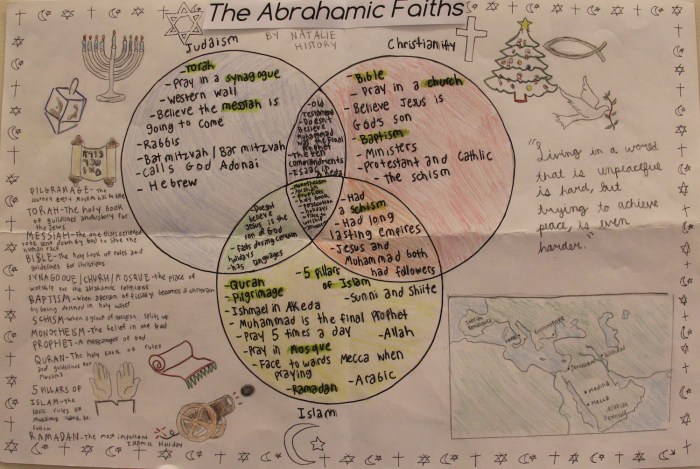
Core Beliefs
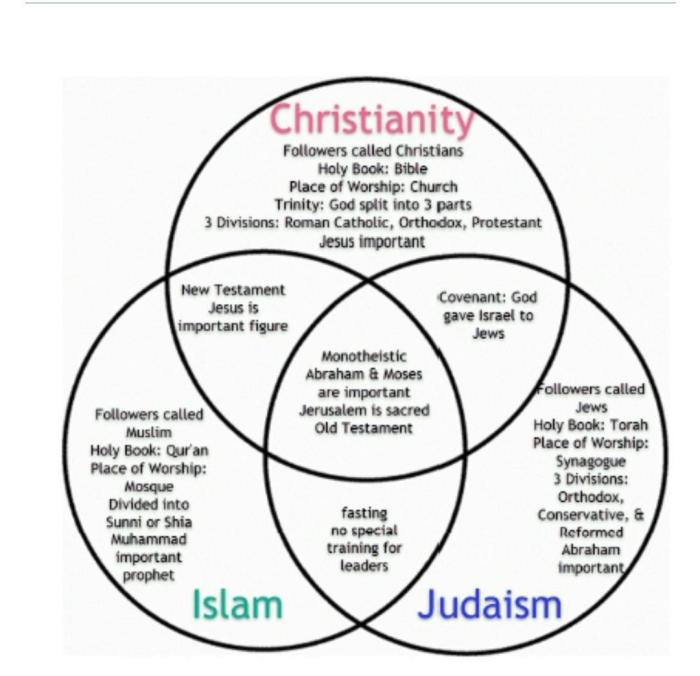
Christianity, Judaism, and Islam share a belief in one God, but their conceptions of God differ. Christianity views God as a Trinity: Father, Son, and Holy Spirit. Judaism emphasizes God’s unity and transcendence. Islam teaches that God is the creator and sustainer of the universe, and Muhammad is his final prophet.
All three religions recognize prophets as messengers of God. Christianity believes in Jesus Christ as the Son of God and the savior of humanity. Judaism reveres Moses as the primary prophet who received the Torah from God. Islam acknowledges Muhammad as the final prophet in a long line of prophets, including Abraham, Moses, and Jesus.
Christianity, Judaism, and Islam each have their own sacred texts. The Christian Bible consists of the Old and New Testaments. The Jewish Torah, also known as the Pentateuch, forms the foundation of the Hebrew Bible. The Muslim Quran is believed to be the final revelation from God and contains the teachings of Muhammad.
Practices and Rituals
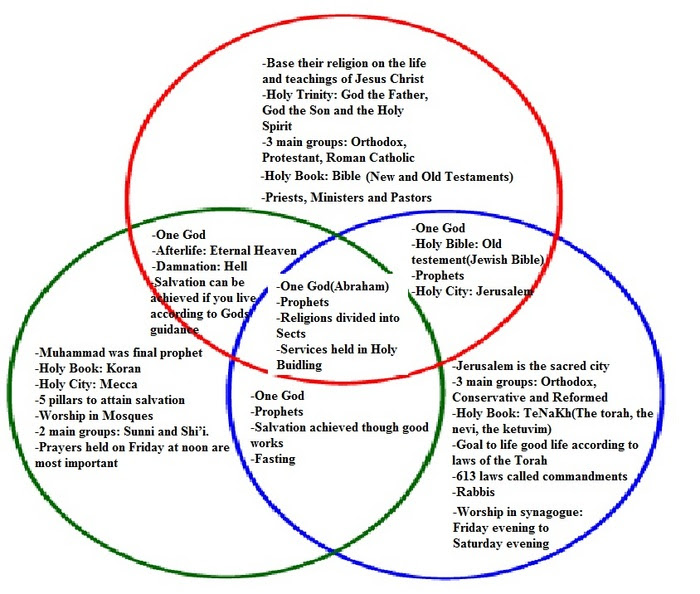
Worship practices vary across the three religions. Christianity involves attending church services, where prayers, hymns, and sermons are central. Judaism focuses on synagogue worship, with prayers, readings from the Torah, and rituals such as the Sabbath and kosher dietary laws.
Islam emphasizes daily prayers, fasting during Ramadan, and the pilgrimage to Mecca.
Prayer is a fundamental practice in all three religions. Christians pray to God through Jesus Christ. Jews pray directly to God, often using the Amidah prayer. Muslims pray five times a day facing Mecca, with specific prayers and rituals.
Festivals are important celebrations in each religion. Christians celebrate Christmas, Easter, and Pentecost. Jews observe Passover, Rosh Hashanah, and Yom Kippur. Muslims celebrate Eid al-Fitr, Eid al-Adha, and the Hajj pilgrimage.
Historical Development: Differences Between Christianity Judaism And Islam Venn Diagram
Christianity emerged in the first century CE as a Jewish sect. Jesus Christ’s teachings and the spread of the gospel by his followers laid the foundation for the religion. Judaism has its roots in ancient Israel and the covenant between God and the Jewish people.
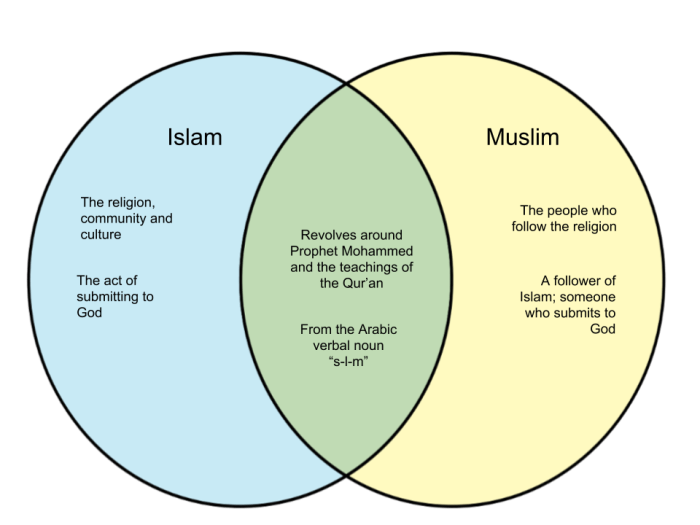
Islam originated in the seventh century CE with the teachings of the Prophet Muhammad. Muhammad received revelations from God, which form the basis of the Quran. Islam rapidly spread throughout the Middle East and beyond.
Key figures and events have shaped the development of each religion. Jesus Christ’s crucifixion and resurrection are central to Christianity. The destruction of the Second Temple in Jerusalem in 70 CE had a profound impact on Judaism. The Battle of Badr in 624 CE was a turning point in the history of Islam.
FAQ Overview
What are the key differences between Christianity, Judaism, and Islam?
The primary differences lie in their beliefs about the nature of God, the role of Jesus Christ, and the authority of religious texts.
How does a Venn diagram help visualize the similarities and differences between these religions?
A Venn diagram provides a clear and concise representation of the overlapping and unique aspects of each religion, allowing for easy comparison and analysis.
What is the significance of the historical development of these religions?
Understanding the historical context helps explain the origins and evolution of their beliefs, practices, and relationships with each other.