Answer key for chemistry matter and change – Unlocking the secrets of matter and change, this answer key provides a comprehensive guide to the fundamental principles of chemistry. From defining matter and change to exploring chemical reactions and energy transformations, this resource empowers students to delve deeper into the captivating world of chemistry.
Embark on a journey through the states of matter, unraveling the transitions between solids, liquids, and gases. Discover the intricate world of chemical reactions, where reactants transform into products, and witness the interplay of energy in chemical processes.
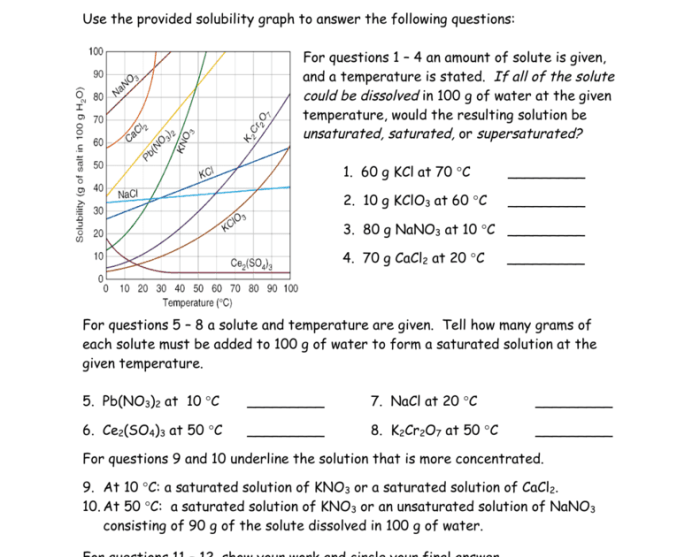
Matter and Change Overview
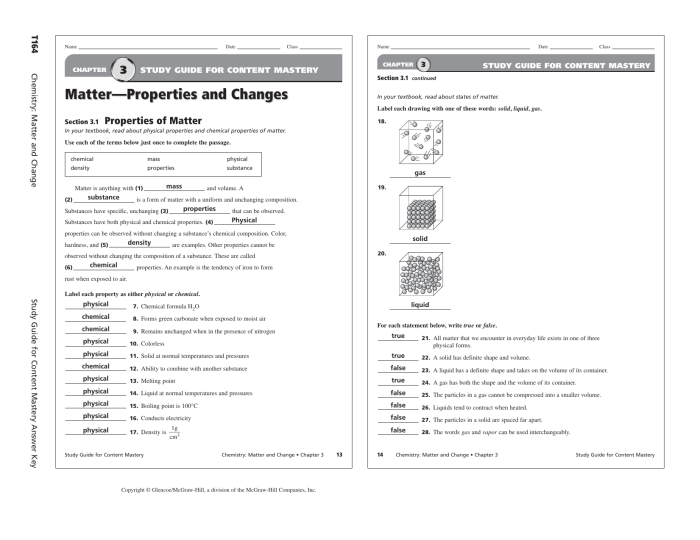
Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. Change is anything that happens to matter.
There are two main types of changes: physical and chemical.
Physical changes are changes in the form or appearance of matter, but not in its chemical composition. Examples of physical changes include melting, freezing, boiling, sublimation, and condensation.
Chemical changes are changes in the chemical composition of matter. Examples of chemical changes include burning, rusting, and cooking.
States of Matter
Matter exists in three states: solid, liquid, and gas.
Solids have a definite shape and volume. Liquids have a definite volume but no definite shape. Gases have no definite shape or volume.
Matter can change states by adding or removing heat. For example, ice (a solid) can be melted into water (a liquid) by adding heat. Water can be boiled into steam (a gas) by adding more heat.
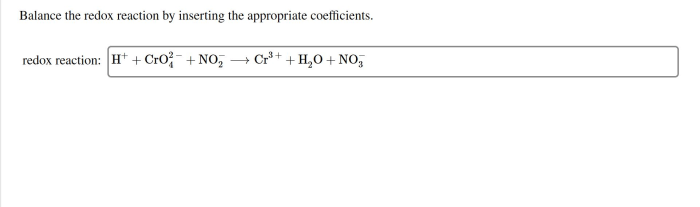
Chemical Reactions, Answer key for chemistry matter and change
A chemical reaction is a process in which one or more substances, the reactants, are transformed into one or more different substances, the products.
Chemical reactions are represented by chemical equations. A chemical equation shows the reactants on the left side of the equation and the products on the right side of the equation. The coefficients in front of the reactants and products show the number of moles of each substance that are involved in the reaction.
For example, the following equation shows the reaction between hydrogen and oxygen to form water:
H2+ O 2→ 2H 2O
Chemical Equations
Chemical equations are used to represent chemical reactions. A chemical equation shows the reactants on the left side of the equation and the products on the right side of the equation. The coefficients in front of the reactants and products show the number of moles of each substance that are involved in the reaction.
The following are the parts of a chemical equation:
- The reactants are the substances that are present at the beginning of the reaction.
- The products are the substances that are formed at the end of the reaction.
- The coefficients are the numbers that appear in front of the reactants and products. The coefficients show the number of moles of each substance that are involved in the reaction.
- The arrow shows the direction of the reaction.
Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry is the study of the quantitative relationships between the reactants and products in a chemical reaction.
Stoichiometry can be used to calculate the amount of reactants and products that are involved in a chemical reaction. For example, the following equation shows the reaction between hydrogen and oxygen to form water:
H2+ O 2→ 2H 2O
This equation tells us that 2 moles of hydrogen react with 1 mole of oxygen to produce 2 moles of water.
Energy Changes in Chemical Reactions
Chemical reactions can involve energy changes. Energy can be released or absorbed during a chemical reaction.
Exothermic reactions are reactions that release energy. For example, the burning of methane is an exothermic reaction.
Endothermic reactions are reactions that absorb energy. For example, the electrolysis of water is an endothermic reaction.
Common Queries: Answer Key For Chemistry Matter And Change
What is the difference between a physical and a chemical change?
A physical change involves a change in the form or appearance of a substance without altering its chemical composition, while a chemical change involves a change in the chemical composition of a substance, creating a new substance with different properties.
How do I write a balanced chemical equation?
A balanced chemical equation represents the conservation of mass in a chemical reaction by ensuring that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation.
What is stoichiometry used for?
Stoichiometry is used to calculate the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in a chemical reaction, allowing for the prediction of the amounts of substances involved.